



Next: Appendices
Up: ISNaS - incompressible flow
Previous: Computation of the stream
- 1
-
C.C. Ashcraft and R.G. Grimes.
On vectorizing incomplete factorization and SSOR preconditioners.
SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput., 9:122-151, 1988.
- 2
-
W.L. Chen, F.S. Lien, and M.A. Leschziner.
Computational modelling of turbulent flow in turbomachine passage
with low-Re two-equation models.
In S. Wagner, E.H. Hirschel, J. Périaux, and R. Piva, editors,
Computational Fluid Dynamics '94, pages 517-524, John Wiley and Sons,
Chicester, 1994.
- 3
-
Y.-S. Chen and S.-W. Kim.
Computations of turbulent flows using an extended k-
 turbulence closure model.
Report NASA CR-179204, NASA-Marshall Space Flight Center, Alabama,
USA, 1987.
turbulence closure model.
Report NASA CR-179204, NASA-Marshall Space Flight Center, Alabama,
USA, 1987.
- 4
-
I.A. Demirdzic.
A finite volume method for computation of fluid flow in complex
geometries.
PhD thesis, University of London, 1982.
- 5
-
S.C. Eisenstat.
Efficient implementation of a class of preconditioned conjugate
gradient methods.
SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput., 2:1-4, 1981.
- 6
-
P.H. Gaskell and K.C. Lau.
Curvature-compensated convective transport: SMART, a new
boundedness-preserving transport algorithm.
Int. J. Numer. Methods in Fluids, 8:617-641, 1988.
- 7
-
T.B. Gatski and C.G. Speziale.
On explicit algebraic stress models for complex turbulent flows.
J. Fluid Mech., 254:59-78, 1993.
- 8
-
V. Haroutunian.
Simulation of vortex shedding past a square prism using three
two-equation turbulence models.
In Sixth Int. Symp. on CFD, volume 1, pages 408-414, Lake
Tahoe, Nevada, 1995.
A collection of technical papers.
- 9
-
C. Hirsch.
Numerical Computation of Internal and External Flows. Vol.1:
Fundamentals of Numerical Discretization.
John Wiley, Chichester, 1988.
- 10
-
M. Kato and B.E. Launder.
The modelling of turbulent flow around stationary and vibrating
square cylinders.
In Proc. Ninth Symposium on Turbulent Shear Flows, volume 9,
page 10.4.1, Kyoto, Japan, 1993.
- 11
-
C.D. Kay.
Schaum's outline of theory and problems of tensor calculus.
McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988.
- 12
-
P. K. Khosla and S. G. Rubin.
A diagonally dominant second-order accurate implicit scheme.
Comput. Fluids, 2:207-209, 1974.
- 13
-
B. Koren.
A robust upwind discretization method for advection, diffusion and
source terms.
In C.B. Vreugdenhil and B. Koren, editors, Numerical methods for
advection-diffusion problems, pages 117-137, Vieweg. Braunschweig,
Wiesbaden, 1993.
Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics 45.
- 14
-
C.K.G. Lam and K. Bremhorst.
A modified form of the k-
 model for predicting wall
turbulence.
ASME J. Fluids Engng., 103:456-460, 1981.
model for predicting wall
turbulence.
ASME J. Fluids Engng., 103:456-460, 1981.
- 15
-
B.E. Launder and D.B. Spalding.
The numerical computation of turbulent flows.
Comp. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 3:269-289, 1974.
- 16
-
F.S. Lien and M.A. Leschziner.
Upstream monotonic interpolation for scalar transport with
application to complex turbulent flows.
Int. J. Num. Meth. Fluids, 19:527-548, 1994.
- 17
-
J.A. Meijerink and H.A. Van der Vorst.
An iterative solution method for linear systems of which the
coefficient matrix is a symmetric M-matrix.
Math. Comp., 31:148-162, 1977.
- 18
-
H.K. Myong and N. Kasagi.
unknown.
J. Fluids Engng., 112:521, 1990.
- 19
-
S. Nisizima and A. Yoshizawa.
Turbulent channel and Couette flows using an anisotropic
k-
 model.
AIAA J., 25:414-420, 1987.
model.
AIAA J., 25:414-420, 1987.
- 20
-
C.C. Paige and M.A. Saunders.
LSQR: an algorithm for sparse linear equations and sparse least
square problem.
ACM Trans. Math. Softw., 8:44-71, 1982.
- 21
-
R. Rubenstein and J.M. Barton.
Non-linear Reynolds stress models and the renormalisation group.
Phys. Fluids A, 2:1472, 1990.
- 22
-
Y. Saad and M.H. Schultz.
GMRES: a generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving
non-symmetric linear systems.
SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comp., 7:856-869, 1986.
- 23
-
H. Schlichting.
Boundary layer theory.
McGraw Hill, New York, 1969.
- 24
-
A. Segal.
The treatment of slip boundary conditions for the incompressible
navier-stokes equations in general co-ordinates.
Report 91-22, Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, Delft
University of Technology, Delft, 1991.
- 25
-
A. Segal and K. Kassels.
Some 2d test examples for the isnas incompressible code.
Report 91-44, Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, Delft
University of Technology, Delft, 1991.
- 26
-
Guus Segal and Kees Kassels.
Improvements of the discretization of the incompressible
Navier-Stokes equations in general coordinates.
Report 96-81, Faculty of Technical Mathematics and Informatics, Delft
University of Technology, Delft, 1996.
- 27
-
P. Sonneveld.
CGS, a fast Lanczos-type solver for nonsymmetric linear systems.
SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput., 10:36-52, 1989.
- 28
-
D.B. Spalding.
A novel finite difference formulation for differential expressions
involving both first and second derivatives.
Int. J. Numer. Methods in Engineering, 4:551-559, 1972.
- 29
-
C.G. Speziale.
On nonlinear k-l and k-
 models of turbulence.
J. Fluid Mech., 178:459-475, 1987.
models of turbulence.
J. Fluid Mech., 178:459-475, 1987.
- 30
-
P.K. Sweby.
High resolution schemes using flux-limiters for hyperbolic
conservation laws.
SIAM J. Num. Anal., 21:995-1011, 1984.
- 31
-
H. Tennekes and J.L. Lumley.
A First Course in Turbulence.
MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachussets, 1982.
- 32
-
H.A. Van der Vorst.
Iterative solution method for certain sparse linear systems with a
non-symmetric matrix arising from PDE-problems.
J. Comput. Phys., 44:1-19, 1981.
- 33
-
H.A. van der Vorst and C. Vuik.
GMRESR: a family of nested GMRES methods.
Num. Lin. Alg. Appl., 1:369-386, 1994.
- 34
-
J.J.I.M. Van Kan, C.W. Oosterlee, A. Segal, and P. Wesseling.
Discretization of the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations in
general coordinates using contravariant velocity components.
Report 91-09, Faculty of Technical Mathematics and Informatics, Delft
University of Technology, Delft, 1991.
- 35
-
B. van Leer.
Towards the ultimate conservative difference scheme. V. A
second-order sequel to Godunov's method.
J. Comput. Phys., 32:101-136, 1979.
- 36
-
C. Vuik.
Termination criteria for GMRES-like methods to solve the
discretizet incompressible navier-stokes equations.
Report 92-50, Faculty of Technical Mathematics and Informatics, Delft
University of Technology, Delft, 1992.
- 37
-
C. Vuik.
Solution of the discretized incompressible Navier-Stokes
equations with the GMRES method.
Int. J. Num. Meth. Fluids, 16:507-523, 1993.
- 38
-
D.C. Wilcox.
Reassessment of the scale determining equation for advanced
turbulence models.
AIAA J., 26:1299-1310, 1988.
- 39
-
D.C. Wilcox.
A half century historical review of the k-
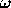 model.
AIAA Paper 91-0615, 1991.
model.
AIAA Paper 91-0615, 1991.
- 40
-
V. Yakhot, S.A. Orszag, S. Thangam, T.B. Gatski, and C.G. Speziale.
Development of turbulence models for shear flows by a double
expansion technique.
Phys. Fluids A, 4:1510-1520, 1992.
- 41
-
M. Zijlema.
On the construction of a third-order accurate TVD scheme with
application to turbulent flows in general domains.
Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids, 1995.
To appear.
- 42
-
M. Zijlema.
Computational modeling of turbulent flows in general domains.
PhD thesis, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands, April
1996.
Tatiana Tijanova
Wed Mar 26 10:36:42 MET 1997