



Next: Prescribed velocities
Up: ISNaS - incompressible flow
Previous: Implementation of the positive
In the present version of the ISNaS incompressible program, the following
types of boundary conditions have been implemented.
Boundary conditions for the momentum equations:
- Type 1:
- Velocity prescribed (Dirichlet boundary condition)
- Type 2:
- Stress prescribed (Natural boundary condition)
- Type 3:
- Normal stress and tangential velocity given (Semi natural
flow)
- Type 4:
- Tangential stress and normal velocity given (Slip boundary
condition and also symmetry condition)
Boundary conditions for the transport equation are:
- Type 1:
- Scalar
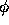 prescribed (Dirichlet boundary condition)
prescribed (Dirichlet boundary condition)
- Type 2:
-
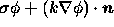 prescribed (Robbins
boundary condition)
prescribed (Robbins
boundary condition)
In the next paragraphs we consider the various boundary conditions
separately.
In 2D the notion normal and tangential vector have been defined in a
somewhat strange way. For a user the normal vector is defined as the
outward normal in the case of a counterclockwise direction and as the
inward normal in the case of
a clockwise direction. The tangential vector is defined in the direction of
the outer boundary. In the program, however, the normal and tangential
vector are always defined in the 1 or 2 direction in the computational
grid. Hence at the boundary 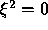 , the normal direction is the
, the normal direction is the
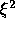 direction and tangential direction the
direction and tangential direction the 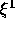 direction. At
the boundary
direction. At
the boundary 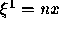 , the normal direction is
, the normal direction is 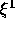 and the
tangential direction
and the
tangential direction 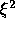 etc.
etc.
In the sequel the internal definition will be used.
Tatiana Tijanova
Wed Mar 26 10:36:42 MET 1997